The Federal Reserve revealed US large banks passed the 2024 banking system stress test as they are projected to be able to absorb a combined close to USD 685 billion of losses under the adverse scenarios and all of them could still meeting the common equity tier 1 (CET1) capital requirements during the hypothetical recession.
The aggregate CET1 capital ratio of the 31 participating banks would fall from 12.7%, the actual ratio as of Q4 2023, to the projected minimum of 9.9%, before rising back to 10.4% in Q1 2026, the end of the stress test projection horizon.
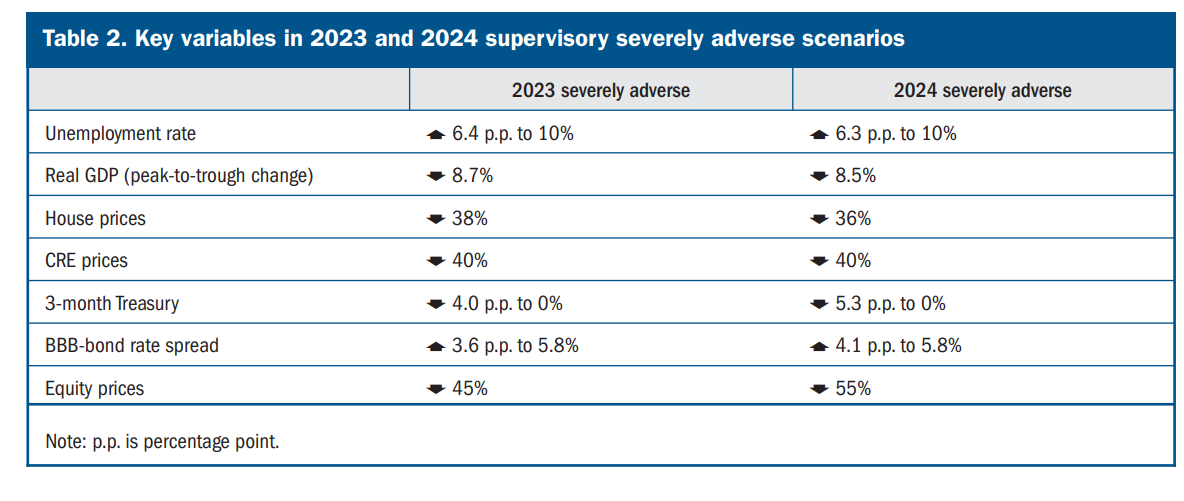
The stress test scenarios assume a severe global recession with sharp rise in unemployment to 10%, substantial fall in equity markets, as well as a period of heightened stress in commercial and residential real estate markets.
The projected 2.8 percentage point decline in the aggregate CET1 capital ratio is larger than the 2.5 percentage point decline estimated in last year’s test. The report cited growth in credit card balances and a rise in credit card delinquencies, riskier corporate credit portfolios as well as
lower noninterest income and higher noninterest expenses as the reasons behind the difference.
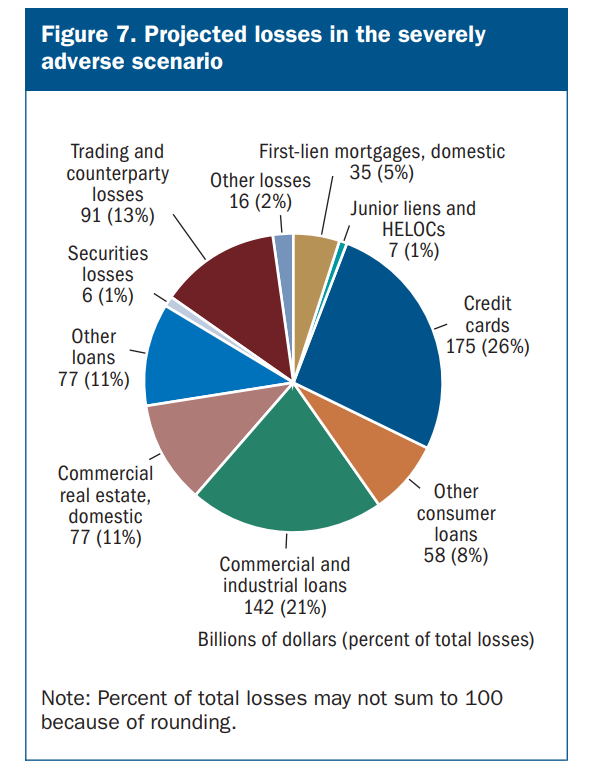
The banks are would to lose an aggregated USD 175 billion on their credit cards business, representing 26% of total projected losses. Commercial and industrial (C&I) loans, of which the non-investment grade loans’ share increased by 2 percentage points over the past year, would contribute to USD 142 billion of projected losses. Losses related to commercial real estate is estimated to be USD 77 billion.
Independent Economics Journalism
Stay ahead of the curve — follow EconReporter for in-depth coverage on economics & markets.