Last Updated:
Canada GDP Monitor: Q3 2025
Net Export-led Rebound vs. Internal Weakness
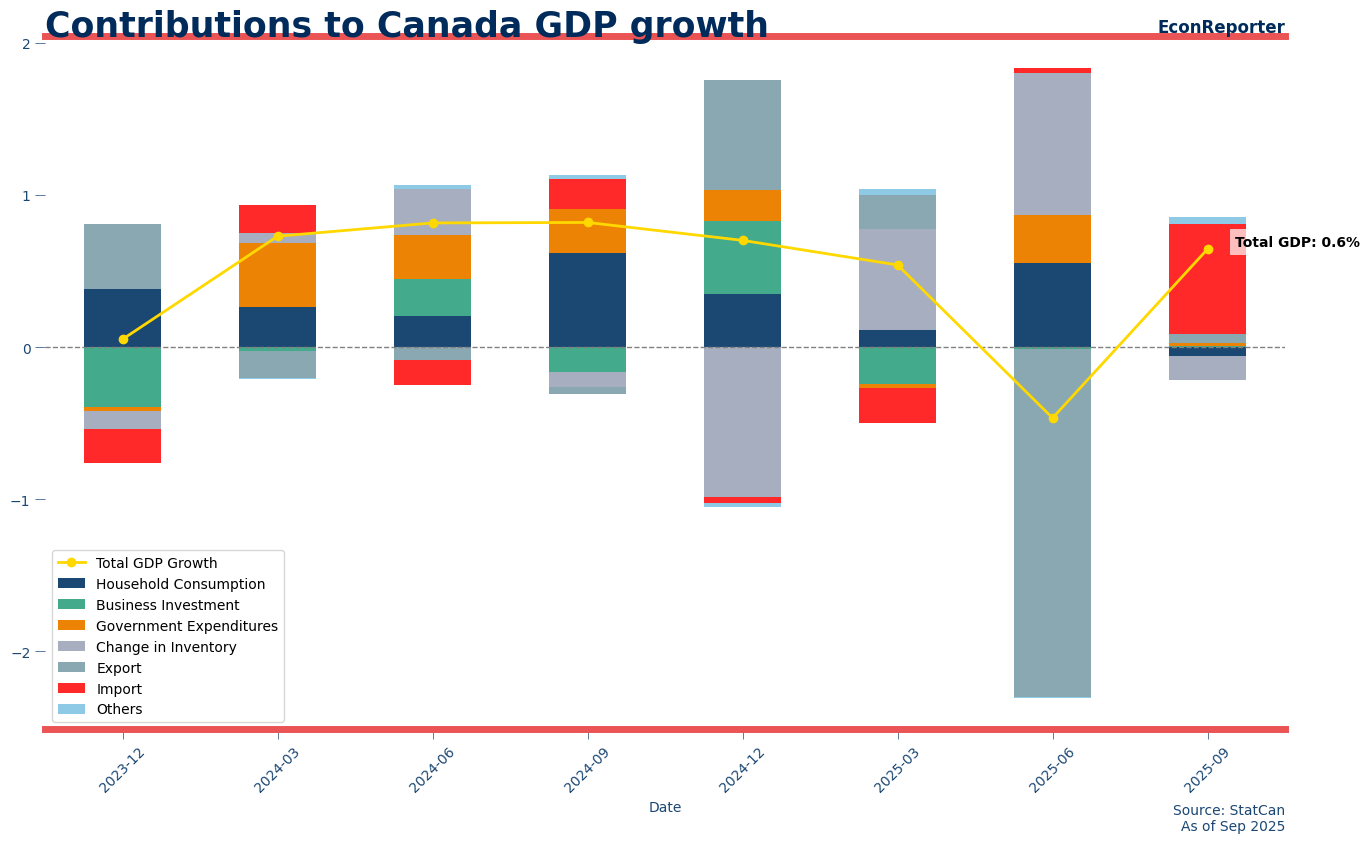
While GDP rebounded by 0.65% in Q3 (2.6% annualized), the expansion was driven almost entirely by a 2.2% drop in imports.
⚠️ Domestic demand turned negative as the internal engine of the economy is stalling.
🫡 Government investment came to recuse
The Numbers: (Q3 vs Q2)
Percentage change in real GDP quarter-over-quarter
| Component | Q3 2025 | Trend | Q2 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total GDP Growth | +0.65% | ✅ Rebound | -0.47% |
| Household Consumption | -0.1% | 📉 Weakening | +1% |
| Business and Government Investment | +0.56% | ➡️ Stalled | +0.23% |
| Government Consumption | -0.44% | 📉 Weakening | +1.17% |
| Exports | +0.18% | 📈 Rebound | -7% |
| Imports | -2.2% | 📉 Weakening | +0.1% |
Analysis
1. The “Import” Illusion
The economic revival was, nonetheless, driven largely by a sharp decline in imports. As can be observed from the contribution graph below, the decline in imports alone accounts for more than 0.7 percentage points (ppt) of the growth; that is even larger than the total growth rate.
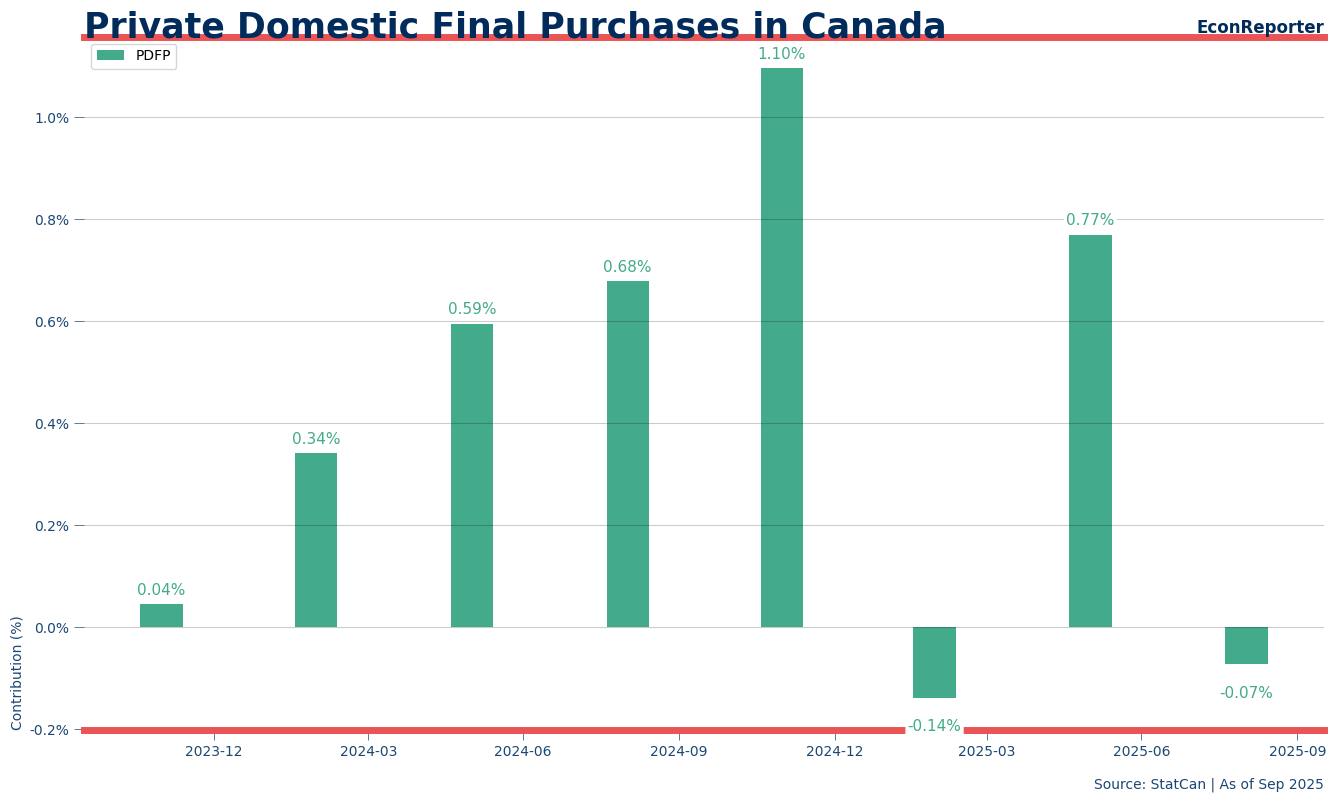
2. The PDFP Warning Signal
A useful way to gauge domestic demand is to look at the so-called Private Domestic Final Purchase (PDFP). This concept, popularized by the Federal Reserve in recent years, serves as an indicator to the domestic demand resiliency in the US economy. Here, it is calculated using Statistics Canada data on household consumption and business gross fixed capital formation.
In Q3, we saw a slight contraction of 0.07%.
Bottom Line: The resilience we saw in household consumption earlier this year has evaporated. With business investment flatlining, the economy is currently “hanging by a thread,” supported only by government spending and readjustment in external trade.
Previous Reports
Access our analysis of previous GDP releases to track the economic trend.
📂 Q2 2025: The Tariff Shock (-0.4%) | Aug 30, 2025
Q2 Summary: Exports Drag Economy Down
Canada’s GDP contracted by 0.4% (1.6% annualized) in the second quarter, primarily due to a massive 7.5% drop in exports as US-imposed tariffs began to bite.
Key Drivers in Q2:
- Exports: Subtracted 2.5 ppts from growth
- Resilience: At this time, household consumption held up well (+0.55 ppt contribution), creating a divergence between domestic and external sectors.
Independent Economics Journalism
Stay ahead of the curve — follow EconReporter for in-depth coverage on economics & markets.